Marketplaces are dynamic ecosystems, and every tweak can have a ripple effect, impacting buyers, sellers, and the overall health of the platform.
Experimentation in such environments is not just beneficial; it's essential. But how do you ensure that your experiments lead to growth without unintended consequences? Enter Statsig, a powerful experimentation platform that's been a game-changer for marketplaces.
In this guide, we'll explore how to leverage Statsig for marketplace experiments, focusing on A/B testing for feature rollouts, pricing strategies, and personalized user experiences. We'll draw from real-world applications by Statsig customers to illustrate successful implementations and outcomes. Plus, we'll delve into best practices for marketplace experiments and how Statsig's tools can optimize them for informed decision-making and growth.
Step-by-step guide to marketplace experiments
Step 1: Defining your experiment goals
Start by identifying what you want to achieve with your experiment. Are you rolling out a new feature, testing a pricing strategy, or personalizing the user experience? Define clear objectives and how they align with your marketplace's strategic goals. Understand the distinction between experiments and feature gates, and when to use which.
Step 2: Setting up your experiment
Statsig's platform offers a seamless setup process for your experiments, and a variety of experiment options:
Feature gates: Use feature gates to control who sees what and when, and/or gradually roll features out and measure performance. For instance, you can introduce a new seller tool to a subset of users and ensure non-inferiority before rolling it out more broadly. For targeting users and/or moving quickly.
A/B/n experiments: Hypothesis-driven, multi-variation experiments. Should drive a conversations around understanding the why and how behind user behavior and product metrics before shipping a variation.
Switchback testing: Ideal for marketplaces, switchback tests help mitigate time-related biases by alternating between treatment and control at different times.
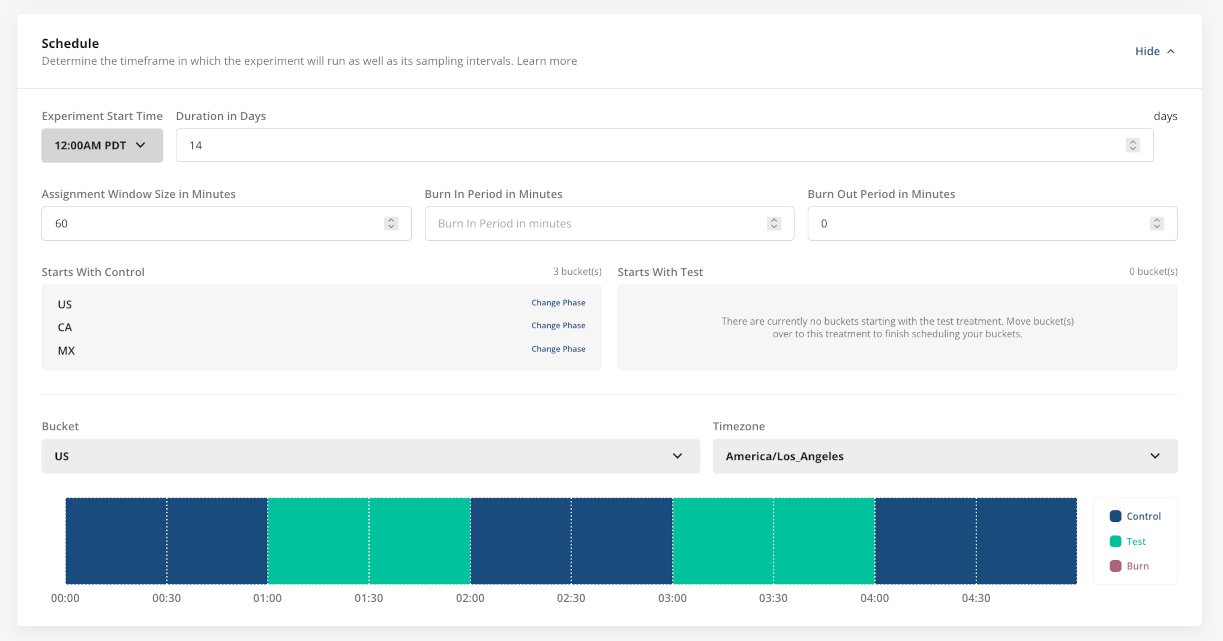
Step 3: Implementing best practices
Network effects: Consider both direct and indirect effects. A change that benefits sellers should not harm buyers, and vice versa.
Switchback testing is particularly common for this reason in marketplaces, whereby running a traditional A/B on one side- or a small %- of the marketplace would have an unintended consequence on the rest of the marketplace due to network effects, ultimately impacting experiment results.
In Statsig, you can create custom metrics that measure buyer side and seller side, further refining analysis.
Segmentation: Understand how different user segments might react to changes and tailor your experiments and analysis accordingly.
Statsig exposes fine grain controls allowing you to build custom inclusion/exclusion criteria.
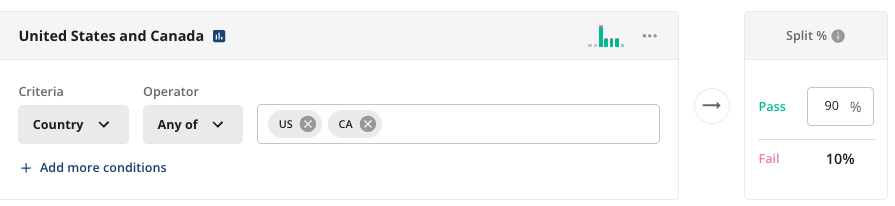
In analysis, Statsig allows you to facet metric analysis by user properties or event properties. You can also filter experiment results based on user groups.
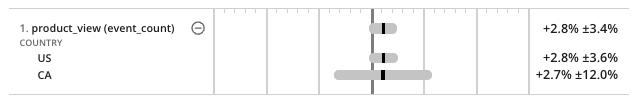
Leverage stratified sampling to ensure equal distribution within test groups.
Cannibalization and spillover effects: Measure both the targeted impact and the broader effects on the marketplace.
Statsig provides the capability to run experiments that can measure both the targeted impact of a feature and its broader effects on the marketplace, which includes assessing cannibalization and spillover effects. By setting up experiments with specific metrics, you can track the primary impact of a change on a targeted segment or feature, as well as monitor secondary metrics that reflect the overall health of the marketplace. This allows you to observe if an increase in one area is causing a decrease in another, indicating cannibalization, or if improvements in one part of the marketplace are positively affecting other areas, indicating spillover benefits.
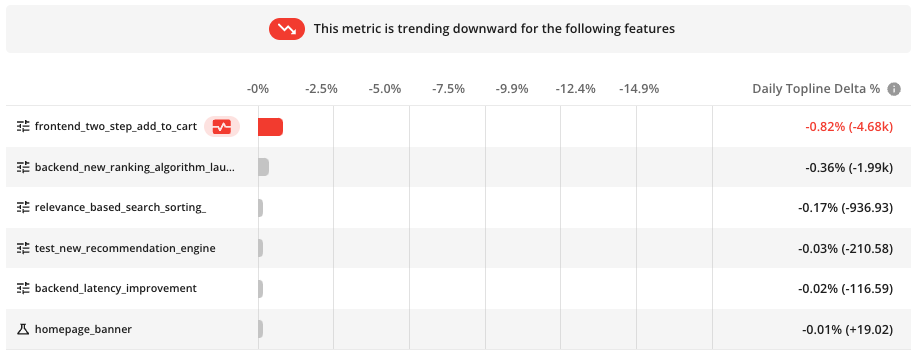
Statsig's experimentation platform allows you to choose any unit of randomization to analyze different user groups, pages, sessions, and other dimensions, which can help in understanding the nuanced effects of experiments across the marketplace. This granular control and analysis help in making informed decisions while considering the interconnected nature of marketplace dynamics.
User experience consistency: Balance experimentation with maintaining a consistent user experience.
Statsig’s user bucketing is deterministic; this makes it consistent across sessions, devices, etc.
Statsig can also facilitate analysis across anonymous to known user funnels.
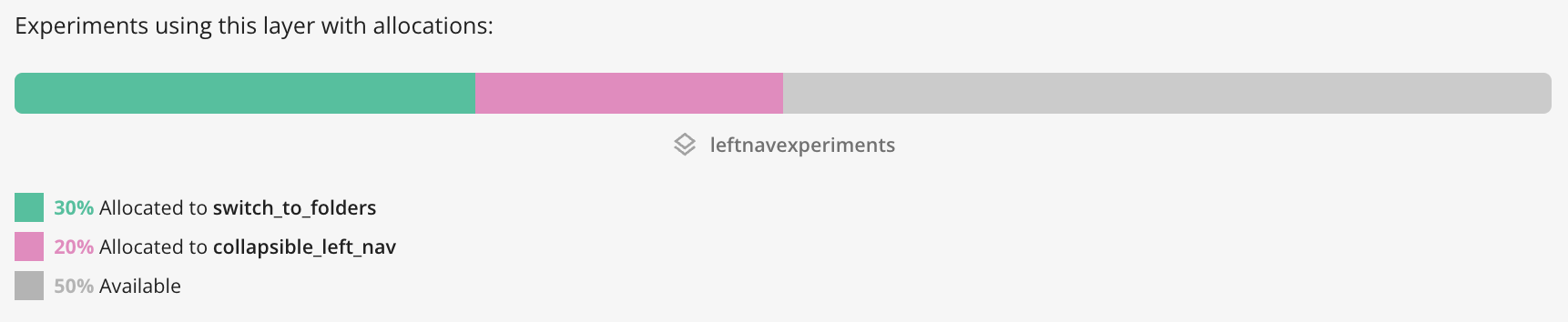
Using Layers in Statsig, you can run sets of experiments mutually exclusively. This will reduce power, but help you ensure a consistent experience on test surfaces.
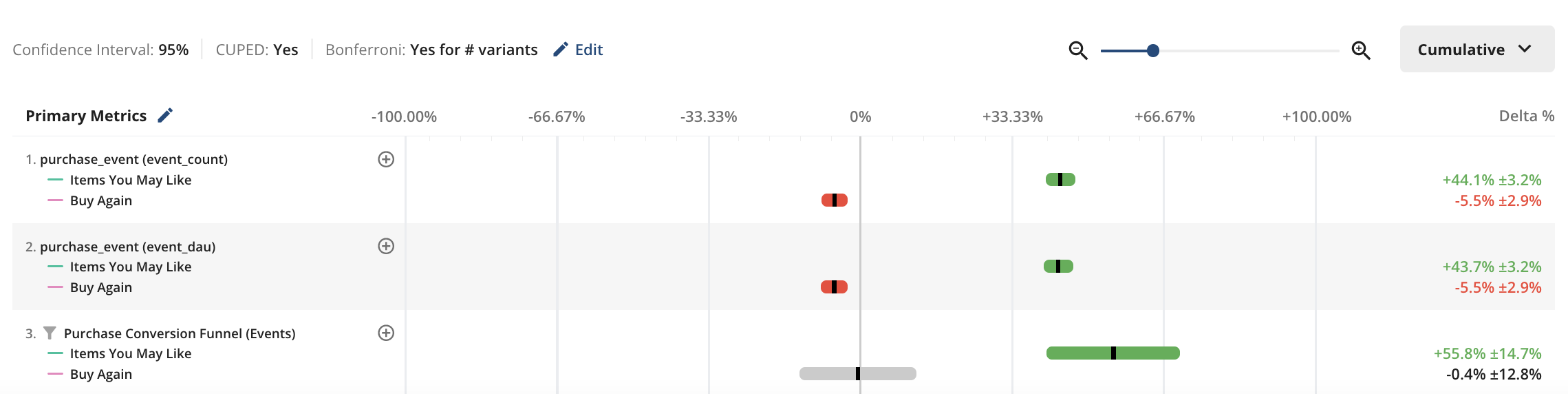
Long-term vs. short-term effects: When evaluating experiment metrics, consider the impact over various timeframes. Unlike some platforms, Statsig doesn't impose time window limits on metrics, allowing for both short and long-term effects to be measured. For example, during an early proof of concept, a customer tested search functionality in their marketplace. Another vendor suggested measuring immediate clicks on search results due to their metric time limits, which favored variant A for its higher click rate. However, by analyzing both immediate and delayed outcomes, Statsig revealed that variant B, despite fewer clicks, led to higher purchase rates and customer lifetime value. This indicated that variant A's increased clicks were not due to better search results but because users struggled to find what they wanted.
Ethical considerations and fairness: Ensure fair treatment and maintain trust in your marketplace.
Statistical rigor: Employ advanced statistical methods to accurately detect causal impacts.
Step 4: Experimentation is a team sport
Statsig offers a robust platform equipped with advanced tooling and analytics to enhance your experimentation results. The experiment scorecard allows for real-time monitoring of crucial metrics, facilitating deep dives into data through custom analyses.
However, to fully leverage Statsig's capabilities, it's essential to foster a strong experimentation culture within your team. Emphasize shared learnings and adhere to best practices.
This involves not only utilizing the tools but also regularly sharing insights, encouraging open discussions, and integrating experimentation into your team's routine. By doing so, Statsig can help you build a data-driven environment that supports continuous improvement and informed decision-making.
Step 5: Learning from real-world applications
Statsig's documentation is rich with customer stories that showcase successful marketplace experiments. For example, OfferUp used Statsig to run mutually exclusive tests, slashing weeks off their development cycle. Lime, on the other hand, leveraged Statsig to test and roll out features like group rides and destination entry, fostering innovation and tackling key business issues.
Happy experimenting!
If you have any questions or feedback on this content, please let us know! For further exploration, dive into Statsig's documentation and join the Statsig slack community of experimenters debugging, sharing insights and tips.
Request a demo